DePIN Explained: Bringing Real-World Devices to Web3
Discover how DePIN merges real-world devices with Web3. Learn how community-owned nodes power new ways to earn and reshape modern infrastructure.

Imagine a world where physical infrastructure—like wireless networks, rendering farms, or even power grids—is owned and operated by everyday people instead of a few large companies. This vision is what DePIN, or Decentralized Physical Infrastructure Network, is bringing to life within Web3. DePIN is gaining attention because it promises to offer new ways to build, maintain, and monetize real-world infrastructure through blockchain technology.
In this article, we’ll explore what DePIN is in Web3, why it matters, and how it’s reshaping traditional models of ownership. By the end, you’ll understand the basics of DePIN, see real-world examples, and discover the opportunities (and challenges) that come with this emerging technology.
Understanding DePIN in Web3
Definition of DePIN
DePIN stands for Decentralized Physical Infrastructure Network. In simpler terms, it’s a system where real-world infrastructure—such as wireless hotspots, computer hardware, or other physical tools—is collectively owned, managed, and operated by a community. Unlike traditional blockchain projects that focus purely on digital transactions or data storage, DePIN projects bring real-world devices and services into the blockchain ecosystem.
Key Terms to Know
- Web3: The next generation of the internet, emphasizing decentralization, user ownership, and blockchain technology.
- Decentralization: Instead of a single company or authority controlling a network, it’s managed by a distributed community.
- Physical Infrastructure: Tangible assets like servers, nodes, antennas, or power stations—anything with a real-world footprint.
Origins and Background
When Bitcoin launched in 2009, the big innovation was a digital currency secured by a decentralized network of computers. Over time, people realized that blockchain’s transparent and secure nature could also improve other areas. We saw smart contracts (allowing programs to run on a blockchain) and decentralized finance (or DeFi, which replaces banks with code).
Then came the next leap: what if we used blockchain principles to manage physical systems, not just digital money? Traditional infrastructure—like cell towers, data centers, and even power grids—tends to be centralized. Major companies or government agencies control them. DePIN aims to distribute that control to many people, making these systems potentially more resilient and user-focused.
Core Principles of DePIN
Decentralized Ownership
Instead of giant corporations or governments owning everything, the community collectively governs the network. This approach can reduce monopolies and encourage widespread innovation.
Incentive Mechanisms
When you contribute something valuable—like hardware or bandwidth—you usually get rewarded with tokens. It’s similar to how Bitcoin miners get paid in Bitcoin, but here the hardware is often more specialized (and tied to real-world services).
Tokenized Economy
Many DePIN projects create their own tokens, which are essential for performing transactions, making governance decisions, and distributing rewards within the ecosystem.
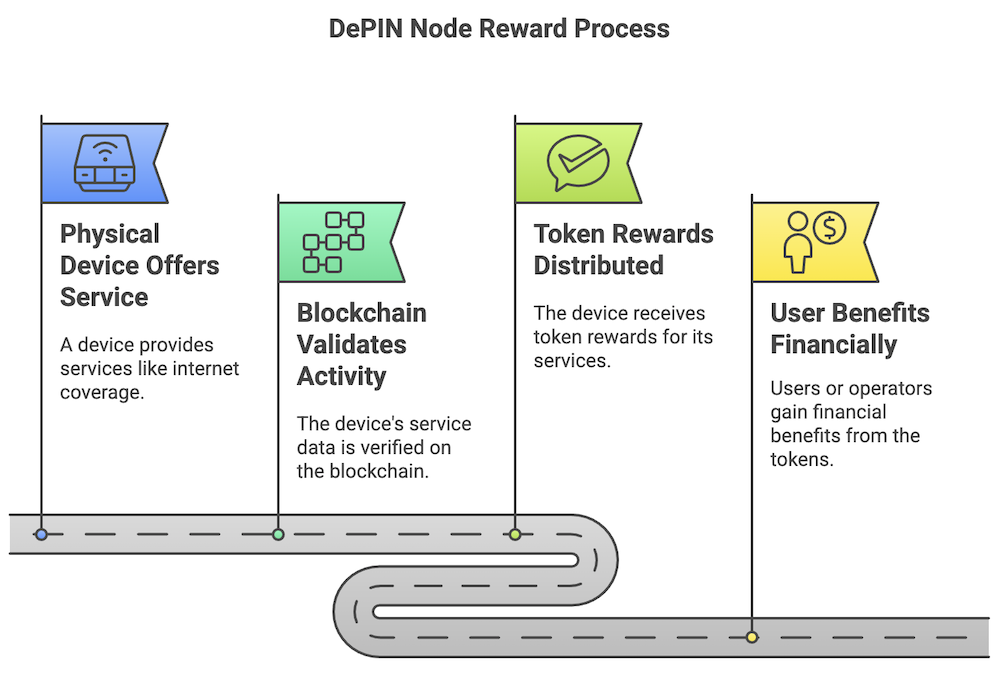
Key Components of DePIN Architecture
Network Nodes and Hardware
In many blockchain projects, running a node might just mean installing software. DePIN often requires physical devices—like wireless Hotspots, GPU servers, or sensors—that provide real-world services. These devices verify transactions or supply necessary operations (such as wireless coverage) to users.
Consensus Mechanisms
Blockchains rely on consensus mechanisms like Proof of Stake (PoS) to confirm transactions. DePIN projects may adapt these or develop new ones like Proof of Coverage, which verifies physical services. The result is a system that rewards participants who genuinely contribute resources to the network.
Security and Data Integrity
One of blockchain’s biggest benefits is its resistance to tampering. Once data is recorded, it’s tough to change. For DePIN, this ensures that the performance of each physical node—such as how much coverage it’s providing—can’t be faked. It keeps the system trustworthy since it’s verified by code and consensus rather than by blind faith in a central authority.
Scalability Concerns
When you add hardware to the mix, scaling can get trickier. For instance, a wireless network can only cover so many devices before it needs more hotspots. And if you’re providing computing power for rendering, what happens when demand skyrockets? DePIN projects often handle these questions by creating incentives that encourage more users to join or by using off-chain solutions (sometimes called “Layer-2”) to help manage high volumes of data.
 Source Helium
Source HeliumReal-World Examples of DePIN Projects
Helium Network
Helium is a decentralized wireless network designed to provide long-range connectivity for IoT (Internet of Things) devices. Individuals deploy Hotspots that offer coverage to surrounding devices in exchange for Helium Network Tokens (HNT).
Operating on the Solana blockchain, Helium relies on a specialized consensus approach called Proof-of-Coverage, ensuring Hotspots actually deliver real network services.
Helium supports diverse IoT applications like smart farming, logistics, and environmental monitoring. By 2025, the Helium community expects to refine Proof-of-Coverage and expand global reach, positioning itself as a top decentralized wireless network.
Render Network (RENDER)
Render Network is a decentralized platform connecting creators seeking to render services with providers who have idle GPU resources. This approach allows tasks such as 3D graphics, animations, and virtual reality content to be distributed across a global pool of computing power.
Looking toward 2025, Render Network aims to improve infrastructure and broaden service offerings, aspiring to lead in decentralized rendering solutions.
Why DePIN Matters: Benefits and Opportunities
Empowering Community Ownership
DePIN shifts control from a handful of corporations to many individual participants. By distributing ownership, communities can reduce monopolies and create fairer, more resilient systems.
Improved Efficiency and Security
A decentralized structure inherently removes single points of failure. When infrastructure is spread across multiple nodes, the entire network can remain operational even if one node experiences issues.
New Business Models and Revenue Streams
For many, DePIN is exciting because it creates a chance to earn rewards by doing more than just “holding” tokens. If you have extra bandwidth, a high-end computer, or even real estate to place a node, you can turn those things into income streams.
Environmental and Social Impact
Some DePIN projects aim to use clean energy or encourage energy efficiency by rewarding nodes that run on lower power. Community-driven governance can also direct resources to causes that matter locally, like connecting rural areas to affordable internet.

DePin Challenges
Technical Complexity
One downside is that you often need specific hardware or technical know-how to participate. Setting up a node can be more involved than just buying crypto on an exchange. Over time, though, user-friendly services and guides may make it easier for ordinary people to join in.
Regulatory Hurdles
The rules around decentralized networks—especially those involving physical devices—are still evolving. Telecom regulations, for example, can vary widely from one country to another. Some DePIN projects might run into legal hurdles about who’s allowed to operate certain types of equipment.
Scalability and Adoption
Even if the technology scales efficiently, real-world constraints like hardware supply and reliable internet connections remain. Massive adoption requires not just advanced tech but also a widespread understanding of how and why to participate.
The Future of DePIN in Web3
Emerging Trends
As 5G, Internet of Things (IoT), and edge computing gain popularity, DePIN could become more valuable. These technologies all involve connecting devices and transferring data. If communities can pool resources to build out that infrastructure, it may create more resilient systems and reduce reliance on giant telecoms or data centres.
Investment and Economic Outlook
Investors are noticing DePIN as a fresh area of Web3. If a project solves a real problem—like providing wireless coverage or offering cheap computing—its tokens may gain value as the network expands. However, it’s important to remember that crypto investments carry risks, including price swings and the potential for regulatory crackdowns.
Next-Generation Use Cases
The concept of decentralized infrastructure opens doors beyond wireless and computing. We might see decentralized power grids, water supply monitoring, or even community-run public transportation tracking. By combining blockchain’s transparency with physical equipment, DePIN holds the potential to remake how we experience everyday services.
Conclusion
DePIN brings blockchain ideas into the physical world. It lets everyday folks own and operate real infrastructure—be it for internet connectivity, computing power, or other essential services. By spreading out ownership and responsibility, DePIN can make these services more accessible, stable, and community-driven.
Projects like Helium and Render Network show that this isn’t just a theory. People all over the globe are already placing devices, earning tokens, and shaping the networks they help run. As new technologies like 5G and IoT become more common, DePIN may well play a key role in ensuring these services are both widely available and more fairly controlled.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What Is the Difference Between DePIN and Traditional Blockchain?
DePIN goes beyond digital transactions by integrating physical infrastructure, whereas traditional blockchains focus mostly on managing and storing digital assets.
How Do DePIN Projects Generate Revenue?
They collect transaction fees, offer paid services (like wireless coverage or compute power), and distribute rewards through the project’s native tokens.
Are DePIN Networks Environmentally Sustainable?
Some networks strive to minimize energy consumption or utilize renewables, but sustainability varies by project. Research each network to assess its specific environmental impact.
Is It Safe to Invest in DePIN Projects?
All crypto investments carry risks, including regulatory changes and market volatility. It’s crucial to do your own due diligence and only invest what you can afford to lose.
How Can I Get Started With DePIN?
Explore official project websites, read community forums, and follow tutorials for setting up node hardware. Many projects provide step-by-step guides for newcomers.
Editor’s note: Written with the assistance of AI – Edited and fact-checked by Jason Newey.





